For many people, reducing or eliminating debt is an important part of improving their financial situation. If you have multiple revolving debt accounts, credit cards or lines of credit with variable interest rates, or loans at high interest rates, you may be able to pay off your debts sooner by combining all of the debts into one loan or credit card with a lower interest rate.
How do you decide what’s the best approach for your particular situation? We’ll break it down into 3 steps.
1. Examine your current payments:
For each loan, credit card, or line of credit you want to consider, gather the following information:
-
The total amount borrowed (the principle)
-
Interest rate
-
Term
-
For revolving debt like credit cards, the minimum payment each month usually includes 1–2% of the amount borrowed.
-
Minimum payment due each month
-
For revolving debt, be sure to note how much of your minimum payment each month goes toward the principle and how much goes toward interest. Most credit cards’ minimum payment is 1–2% of the principle PLUS any accrued interest.
-
You might also want to calculate how much interest you will pay total over the length of the debt.
Calculate the total amount you pay now each month for all of these debts combined. Here's a sample of one person's debts:
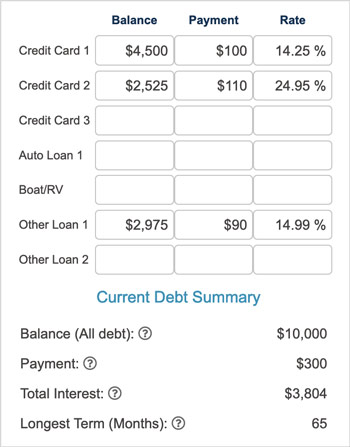
2. Consider consolidation options:
At GE Credit Union, we have three primary options for helping members consolidate their debt: Debt Consolidation Loans (Personal Loans), Home Equity Loans, and Credit Card Balance Transfers. You can take the debt information you gathered above and look at various consolidation scenarios using the Credit Calculators on our website or keep reading to see how each of these options play out for our imaginary member.
Calculate the monthly payment, how long it will take you to pay off your debt, and the total amount of interest paid over the life of the loan. Hopefully, you will find an option with a lower monthly payment, shorter payment term, or both. Chose an option that suits your budget and helps you pay off that debt once and for all!
-
Debt Consolidation Loan (personal loan): These loans enable you to pay back a set amount each month over a fixed term and with a fixed interest rate. That means your payment will be the same each month and cannot increase. Debt consolidation loans are available for up to $15,000 over a 60-month term.
Using our example above of the person who owes $10,000, their monthly payments would look like this:
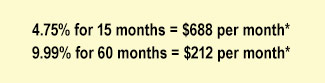
-
Home Equity Loan: If you own a home and owe less than it’s worth, you can leverage the difference (your equity) as collateral for a loan. Home Equity Loans are available for terms up to 20 years depending on the amount and also come with a fixed interest rate, so your monthly payment will never increase.
Using our example above of the person who owes $10,000, their monthly payments would look like this:

-
Credit Card Balance Transfer: While a loan with a low fixed rate (and no ability to take on additional debt) may be the preferred solution for some, a credit card balance transfer might make sense for others. GE Credit Union offers a special 7.99% APR on balance transfers until paid in full plus a one-time 3.0% balance transfer fee.
Using our example above of the person who owes $10,000, a credit card balance transfer would look like this
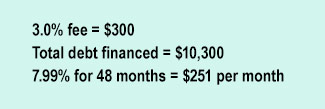
3. Beyond consolidation: Learning to live without debt
If you have been struggling to pay off revolving debt and are committed to moving beyond that phase of your life, once you consolidate your current debt into a single loan or payment plan, it’s key to not take on additional debt. You should consider closing your existing revolving debt accounts once the balance is transferred so that you don’t continue to take spend more than you can afford. In fact, you may find that your lender will make a consolidation loan to you only on the condition that you close the other accounts.